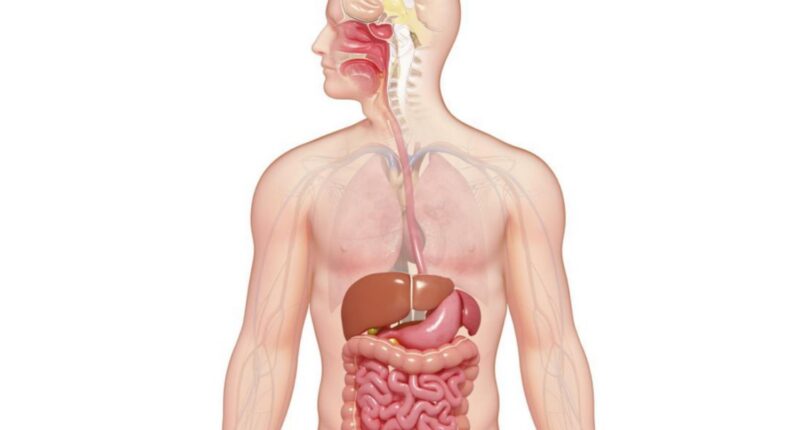
Your gut microbiome is a vibrant ecosystem made up of trillions of microorganisms, such as bacteria, fungi, and viruses, that inhabit your digestive system. While this might sound unsettling, these tiny inhabitants play a crucial role in maintaining your overall health, particularly your digestive system. A balanced and healthy gut microbiome can help improve digestion, enhance nutrient absorption, and even boost your immune system. Here’s everything you need to know about the gut microbiome and its impact on your digestive health.
What Is the Gut Microbiome?
The gut microbiome refers to the diverse ecosystem of microorganisms residing in your gastrointestinal tract. These microbes play a crucial role in our health by breaking down complex carbohydrates, producing essential vitamins like B12 and K, and bolstering our immune system. Although some bacteria in the gut can be harmful, the beneficial ones significantly outnumber the harmful types in a healthy microbiome, which helps ensure smooth digestive function.
The Importance of Gut Microbiome in Digestive Health?
A well-balanced gut microbiome offers several benefits for your digestive health:
- Efficient Digestion: The gut microbiome aids in breaking down food particles that your stomach and intestines cannot digest on their own. This process allows you to better absorb the nutrients from the food you consume.
- Preventing Digestive Disorders: An imbalanced gut microbiome, also known as dysbiosis, can lead to issues such as bloating, diarrhoea, constipation, and irritable bowel syndrome (IBS).
- Strengthening Gut Barrier: The gut microbiome supports the integrity of the gut lining, preventing harmful pathogens and toxins from entering the bloodstream.
- Reducing Inflammation: Some beneficial bacteria produce short-chain fatty acids (SCFAs), which help reduce inflammation in the gut and support overall digestive health.
Factors That Impact Your Gut Microbiome
Your gut microbiome’s balance is significantly influenced by a range of lifestyle and environmental factors, making it crucial to pay attention to these aspects for your overall health.
- Diet: The foods you consume play a crucial role in influencing your gut health. A diet rich in processed and sugar can disrupt the balance, while fibre-rich foods promote a diverse and healthy microbiome.
- Antibiotics: While antibiotics treat infections, they can also kill beneficial bacteria, leading to an imbalance.
- Stress: Chronic stress can alter the composition of your gut microbiome, affecting digestion and overall health.
- Sleep: Poor sleep patterns can negatively affect gut bacteria, reducing their diversity and functionality.
How to Support a Healthy Gut Microbiome
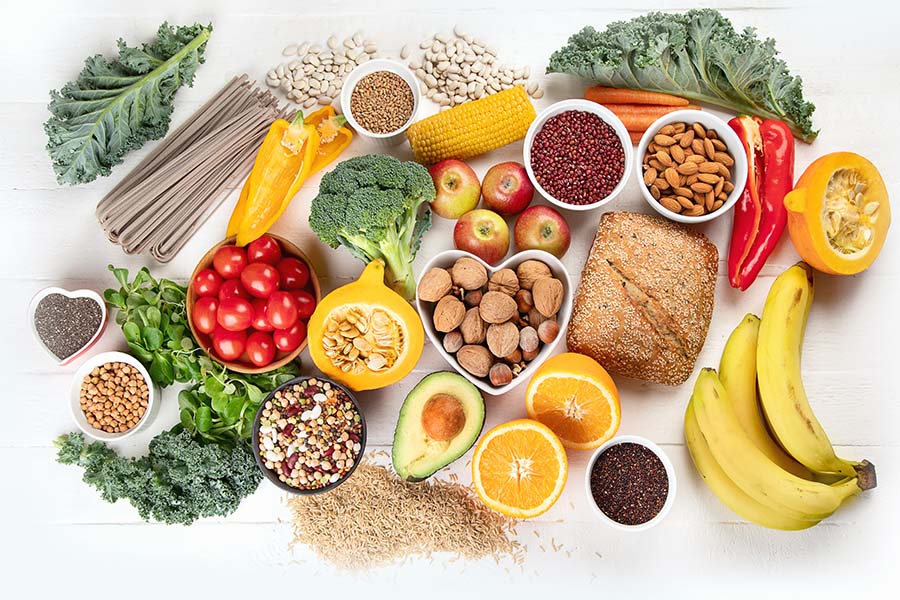 Taking care of your gut microbiome is essential for upholding digestive health. Here are some effective ways to nurture it:
Taking care of your gut microbiome is essential for upholding digestive health. Here are some effective ways to nurture it:
- Eat a Fiber-Rich Diet
Dietary fibre feeds the beneficial bacteria in your gut. Foods like fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and legumes provide prebiotics—non-digestible fibres that stimulate the growth of healthy bacteria.
- Incorporate Probiotic Foods
Probiotics are live microorganisms that can restore the balance of your gut microbiome. Fermented foods like yoghurt, kefir, kimchi, sauerkraut, and miso are excellent sources of probiotics.
- Avoid Processed Foods
Minimize the consumption of processed foods, added sugars, and artificial sweeteners, as they can disrupt the balance of your gut bacteria.
- Stay Hydrated
Proper hydration supports the mucosal lining of the intestines and promotes the growth of beneficial bacteria. Aim to drink plenty of water daily.
- Manage Stress
Chronic stress can negatively affect your gut microbiome. To manage stress, practice stress-management techniques like yoga, meditation, or deep breathing exercises.
- Get Enough Sleep
To maintain a healthy gut microbiome, prioritize quality sleep. Aim for 7-9 hours of sleep per night and maintain a consistent sleep schedule.
- Consider Supplements
Probiotic supplements can help replenish good bacteria, especially after a course of antibiotics. Prebiotic supplements, which feed probiotics, may also be beneficial. Always consult your healthcare provider before starting any supplements.
Signs of an Unhealthy Gut Microbiome
How do you know if your gut microbiome is imbalanced? Common signs include:
- Frequent bloating, gas, or abdominal discomfort
- Irregular bowel movements (constipation or diarrhoea)
- Increased food intolerances
- Persistent fatigue or low-energy
- Skin conditions like acne or eczema
- A weakened immune system
If you experience these symptoms consistently, it might be time to evaluate your gut health.
Conclusion
Your gut microbiome serves as the cornerstone of your digestive health, playing a crucial role in everything from nutrient absorption to immune system function. Maintaining a healthy gut microbiome involves adopting a balanced diet, managing stress, staying hydrated, and ensuring sufficient sleep. By taking proactive steps to care for your gut, you can enhance not only your digestive health but also your overall well-being.
A balanced gut microbiome is the key to feeling your best, so make it a priority today!