Diabetes is a chronic condition that affects millions of people worldwide. Proper management is crucial for improved quality of life. In this article, we delve into the intricacies of diabetes, exploring its types, causes, symptoms, management strategies, and the importance of lifestyle modifications.

Types of Diabetes:
There are primarily three types of diabetes: type 1, type 2, and gestational diabetes. Type 1 diabetes is an autoimmune condition where the immune system attacks insulin-producing cells in the pancreas, leading to insulin deficiency. Type 2 diabetes develops when the body either cannot produce enough insulin or becomes resistant to insulin. Gestational diabetes develops during pregnancy and typically resolves after childbirth, but it can increase the risk of type 2 diabetes later in life.
Causes and Risk Factors of Diabetes:
The exact causes of diabetes vary depending on the type. Type 1 diabetes is believed to have genetic and environmental factors, while type 2 diabetes is closely linked to lifestyle factors such as obesity, physical inactivity, and unhealthy eating habits. Other risk factors for diabetes include family history, ethnicity (e.g., South Asian, Black, Hispanic), age, and certain medical conditions like polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS).
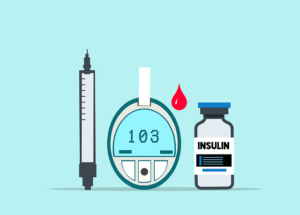
Symptoms and Diagnosis of Diabetes:
Common symptoms of diabetes include frequent urination, excessive thirst, unexplained weight loss, fatigue, blurred vision, slow wound healing, and recurrent infections. To diagnose diabetes, one needs to undergo blood tests that help measure the levels of sugar in the blood. A fasting plasma glucose test, oral glucose tolerance test, or glycated haemoglobin (HbA1c) test may be used to diagnose diabetes or assess blood sugar control in those already diagnosed.
Management Strategies of Diabetes:
Managing diabetes effectively requires a comprehensive approach that includes:
1. Diet: Adopting a balanced diet rich in whole grains, fruits, vegetables, lean proteins, and healthy fats can help regulate blood sugar levels. Avoiding sugary drinks, refined carbs, and excessive salt and fat is crucial.
2. Physical Activity: Regular exercise improves insulin sensitivity and helps control blood sugar levels. Try to do 150 minutes of moderate aerobic exercise every week, and muscle-strengthening exercises twice a week.
3. Medication: Depending on the type and severity of diabetes, medication may be necessary to control blood sugar. This can include insulin injections, oral medications (e.g., metformin), or other injectable drugs.
4. Monitoring: Regularly monitoring blood sugar levels using glucometers or continuous glucose monitoring systems allows for timely adjustments in medication, diet, and exercise routines.
5. Education and Support: Diabetes education programmes provide valuable information on self-care, medication management, meal planning, and coping strategies. Support from healthcare professionals, family, and peers can also enhance diabetes management and emotional well-being.
Importance of Lifestyle Modifications:
Lifestyle changes are crucial for managing and preventing diabetes. Maintaining a healthy weight, staying physically active, quitting smoking, limiting alcohol consumption, managing stress effectively, and getting regular check-ups are essential components of a diabetes-friendly lifestyle. Small but consistent changes can yield significant long-term benefits in diabetes control and overall health.
Diabetes is a complex condition that requires diligence, education, and a proactive approach to management. By understanding the types, causes, symptoms, and effective strategies for managing diabetes, individuals can lead fulfilling lives while minimising the risk of complications. Remember, diabetes management is a journey that requires an ongoing commitment to healthy choices and regular communication with healthcare providers. With the right tools and support, thriving with diabetes is not only possible but achievable.