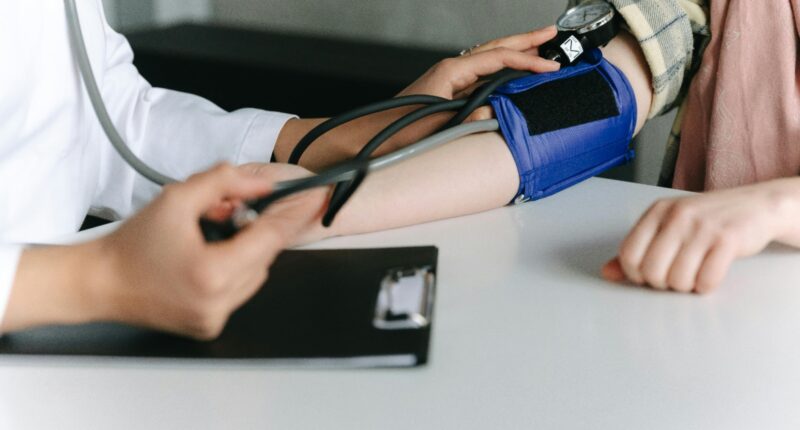
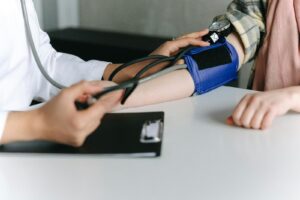
Hypertension, commonly known as high blood pressure, is a prevalent cardiovascular condition affecting millions of people worldwide. Let’s explore the causes, effects, risk factors, and management strategies for hypertension, shedding light on this silent but significant health concern.
What is Hypertension?
Hypertension is a medical condition characterized by elevated blood pressure levels persistently exceeding the normal range. Blood pressure is measured in millimetres of mercury (mmHg) and is expressed as two numbers: systolic pressure (when the heart contracts) and diastolic pressure (when the heart relaxes). Normal blood pressure is typically defined as less than 120/80 mmHg.
Causes of Hypertension:
1. Lifestyle Factors: Unhealthy lifestyle choices such as a sedentary lifestyle, poor dietary habits (high sodium, low potassium), excessive alcohol consumption, smoking, and chronic stress can contribute to hypertension.
2. Genetic Factors: Family history of hypertension or genetic predisposition to high blood pressure can increase the risk of developing the condition.
3. Obesity: Being overweight or obese puts additional strain on the heart and blood vessels, leading to higher blood pressure.
4. Medical Conditions: Certain medical conditions such as kidney disease, thyroid disorders, sleep apnoea, and adrenal gland disorders can contribute to hypertension.
5. Age and Gender: As individuals age, and particularly in males, there is a higher likelihood of developing hypertension or high blood pressure.
Effects of Hypertension:
Untreated or poorly controlled hypertension can have serious health consequences and lead to various complications, including:
– Increased risk of heart disease, heart attacks, and heart failure
– Stroke and transient ischemic attacks (TIAs)
– Kidney damage and chronic kidney disease
– Vision problems and retinopathy
– Peripheral artery disease (PAD) and circulation issues
– Cognitive decline and dementia
Managing Hypertension:
Effective management of hypertension involves a combination of lifestyle modifications, medication adherence, regular monitoring, and ongoing medical care. Here are key strategies for managing hypertension:
1. Healthy Diet: Adopt a balanced and heart-healthy diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and low-fat dairy products. Limit sodium intake, avoid processed foods, and reduce consumption of saturated and trans fats.
2. Regular Physical Activity: Engage in regular aerobic exercise such as brisk walking, jogging, cycling, or swimming for at least 30 minutes most days of the week. Physical activity helps lower blood pressure, improve cardiovascular health, and manage weight.
3. Weight Management: Achieve and maintain a healthy weight through a combination of healthy eating, regular exercise, and portion control. Significant reduction in blood pressure levels can be achieved by losing excess weight.
4. Limit Alcohol and Quit Smoking: Limit alcohol consumption to moderate levels (if consumed) and avoid smoking or tobacco use, as they can raise blood pressure and increase the risk of heart disease.
5. Medication Adherence: If prescribed by a healthcare provider, take medications as directed to control blood pressure effectively. Common medications for hypertension include diuretics, ACE inhibitors, beta-blockers, calcium channel blockers, and angiotensin II receptor blockers (ARBs).
6. Stress Management Practice: stress-reducing techniques such as deep breathing, meditation, yoga, mindfulness, and relaxation exercises to manage stress levels and promote overall well-being.
7. Regular Monitoring: Monitor blood pressure regularly at home using a reliable blood pressure monitor. Keep track of readings and share them with your healthcare provider during check-ups.
Importance of Hypertension Awareness
Raising awareness about hypertension, its risk factors, and preventive measures is crucial in combating this silent but significant health condition. Public education, community outreach, healthcare initiatives, and screening programmes play a vital role in early detection, timely intervention, and improved outcomes for individuals with hypertension.
Hypertension is a common yet manageable cardiovascular condition that requires proactive lifestyle changes, medication management, and regular monitoring. By adopting a heart-healthy lifestyle, maintaining a healthy weight, adhering to prescribed treatments, and seeking regular medical care, individuals can effectively manage hypertension, reduce the risk of complications, and improve overall cardiovascular health. Hypertension awareness, education, and preventive strategies are key in promoting optimal health and well-being for individuals of all ages.