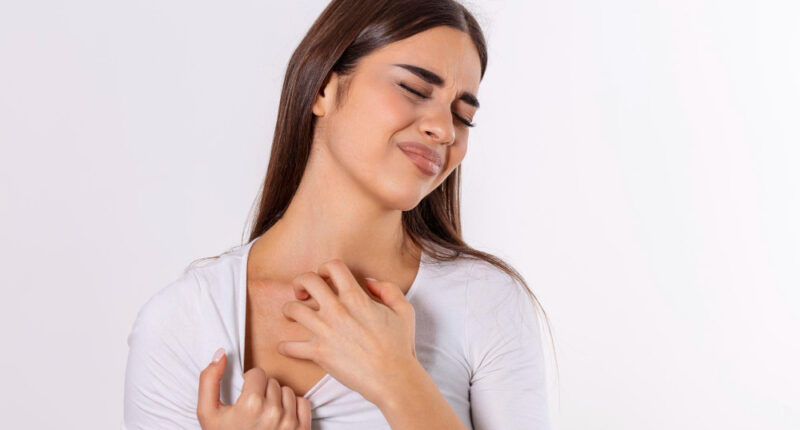
Eczema, also known as atopic dermatitis, is a prevalent skin condition that impacts millions of individuals globally. Characterized by dry, itchy, and inflamed skin, eczema can significantly impact the quality of life. This comprehensive guide will delve into the causes, symptoms, and treatments of eczema, offering valuable insights for managing this chronic condition.
What is Eczema?
Eczema is a chronic inflammatory skin condition that often begins in childhood but can occur at any age. It causes the skin to become red, itchy, and swollen. The severity of eczema can vary from mild patches of dry skin to severe, widespread inflammation.
Causes of Eczema
While the precise cause of eczema remains unclear, it is widely believed to stem from a complex interplay of genetic and environmental factors. Some common triggers include:
Genetics:
A family history of eczema, asthma, or hay fever increases the risk of developing eczema.
Immune System Dysfunction:
An overactive immune system response can lead to inflammation and eczema flare-ups.
Environmental Factors:
Exposure to irritants such as soaps, detergents, or chemicals can aggravate eczema.
Allergens like pollen, pet dander, or dust mites can trigger symptoms.
Climate:
Extreme temperatures and humidity levels can worsen eczema symptoms.
Stress:
Emotional stress can exacerbate eczema flare-ups.
Diet:
Certain foods, including dairy, nuts, and wheat, can trigger eczema in some individuals.
Symptoms of Eczema
Eczema symptoms can manifest in a variety of ways, but some common signs to look out for include:
Dry, Sensitive Skin:
The skin becomes excessively dry and sensitive to touch.
Itching:
Intense itching, often worse at night, is a hallmark of eczema.
Red, Inflamed Skin:
Patches of red, inflamed skin are common, especially on the hands, feet, face, and neck.
Blisters:
In severe cases, blisters may form, which can ooze and crust over.
Thickened Skin:
Chronic scratching can lead to thick, leathery patches of skin.
Darkened Skin Patches:
Affected areas may become darker due to chronic inflammation and irritation.
Diagnosing Eczema
Diagnosis is typically made based on the appearance of the skin and a review of the patient’s medical history. In some cases, a dermatologist may perform a skin biopsy or allergy tests to rule out other conditions and identify specific triggers.
Treatment Options for Eczema
While there is no cure for eczema, various treatments can help manage symptoms and prevent flare-ups. The treatment plan often involves a combination of lifestyle changes, topical treatments, and, in some cases, systemic medications.
Moisturizing:
Regularly applying moisturizers helps maintain the skin’s barrier and prevent dryness. Use fragrance-free and hypoallergenic products.
Topical Steroids:
Corticosteroid creams and ointments reduce inflammation and itching. Use them as directed by a healthcare provider.
Topical Calcineurin Inhibitors:
These medications, such as tacrolimus and pimecrolimus, help reduce inflammation and are suitable for sensitive skin areas like the face and neck.
Antihistamines:
Oral antihistamines can help alleviate itching, especially at night.
Wet Wrap Therapy:
Applying wet bandages over moisturizer or topical medications can help hydrate the skin and reduce inflammation.
Phototherapy:
Exposure to ultraviolet (UV) light under medical supervision can improve severe eczema.
Systemic Medications:
In severe cases, oral or injectable medications like corticosteroids, cyclosporine, or biologics may be prescribed to control symptoms.
Lifestyle and Home Remedies
In addition to medical treatments, lifestyle changes can help manage eczema symptoms:
Avoid Triggers:
Identify and avoid known irritants and allergens that trigger eczema flare-ups.
Bathe Properly:
Use lukewarm water and mild, fragrance-free cleansers. Limit bath time to 10-15 minutes and moisturize immediately after bathing.
Wear Soft Fabrics:
Choose clothing made of soft, breathable materials like cotton. Avoid wool and synthetic fabrics that can irritate the skin.
Manage Stress:
Practice stress-reducing techniques such as meditation, yoga, or deep-breathing exercises.
Stay Hydrated:
Drink plenty of water to keep the skin hydrated from within.
Conclusion
Eczema is a challenging condition, but with the right treatment and lifestyle adjustments, it can be effectively managed. Understanding the causes, recognizing the symptoms, and following a tailored treatment plan are crucial steps in controlling eczema and improving the quality of life. If you or your child suffers from eczema, consult a healthcare provider to develop a comprehensive management strategy tailored to your needs.