Cholesterol is a vital substance in the body, but having too much of it can lead to serious health issues. Understanding what cholesterol is, its types, and how to manage it effectively is crucial for maintaining heart health and overall well-being. This comprehensive guide will delve into everything you need to know about cholesterol.
What is Cholesterol?
Cholesterol is a type of waxy, fat-like substance that is present in all the cells of the human body. It plays a crucial role in the production of hormones, vitamin D, and substances that aid in the digestion of foods. Your body makes all the cholesterol it needs, but cholesterol is also found in foods from animal sources, such as meat, cheese, and eggs.
Types of Cholesterol
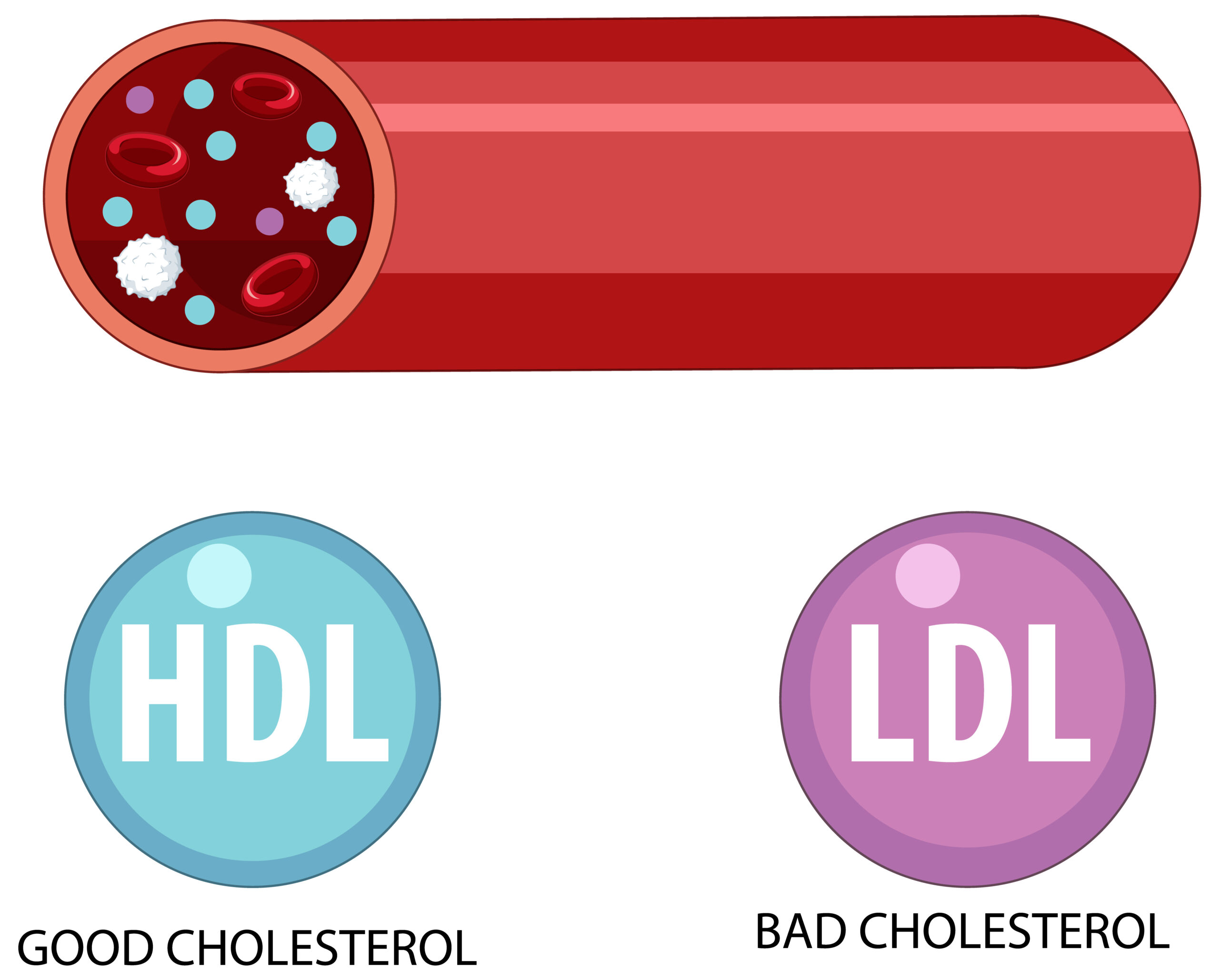
Cholesterol travels through your bloodstream attached to proteins. Lipoproteins are the dynamic duo of proteins and cholesterol working together in the body. There are two main types of cholesterol based on the type of lipoprotein:
- Low-Density Lipoprotein (LDL):
- LDL, also known as “bad” cholesterol, is responsible for transporting cholesterol particles throughout your body. High levels of LDL cholesterol can lead to the buildup of plaques in your arteries, causing them to narrow and harden. Heart disease, heart attack, and stroke are spiked by LDL.
- High-Density Lipoprotein (HDL):
- Known as “good” cholesterol, HDL picks up excess cholesterol and takes it back to your liver, where it’s processed and removed from your body. Having high levels of HDL cholesterol can significantly lower your risk of heart disease.
Causes of High Cholesterol
High cholesterol is caused by several factors, some of which are:
- Diet:
- Eating foods high in saturated fats, trans fats, and cholesterol can raise your cholesterol levels. Foods such as red meat, full-fat dairy products, and processed items are often the main culprits behind certain health issues.
- Lack of Exercise:
- Physical inactivity can lead to weight gain and higher levels of LDL cholesterol. Regular exercise helps increase HDL cholesterol.
- Genetics:
- High cholesterol can run in families. Genetic factors can affect how your body processes cholesterol.
- Obesity:
- Excess weight tends to increase LDL cholesterol and decrease HDL cholesterol.
- Age and Gender:
- Cholesterol levels naturally rise as you get older. Before menopause, women generally have lower total cholesterol levels than men of the same age. After menopause, women’s LDL levels tend to rise.
Symptoms of High Cholesterol
High cholesterol itself does not cause symptoms. The only way to know if you have it is through a blood test. However, high cholesterol can lead to conditions that have symptoms, such as chest pain (angina) or heart attack due to coronary artery disease.

How to Manage Cholesterol
Managing cholesterol involves lifestyle changes and, in some cases, medication. Here are effective strategies to maintain healthy cholesterol levels:
- Healthy Diet:
- Eat Heart-Healthy Foods:Remember to prioritize fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins in your diet. Consider incorporating foods high in omega-3 fatty acids like salmon, walnuts, and flaxseeds to help reduce LDL cholesterol levels.
- Avoid Trans Fats:Found in many fried and commercially baked products, trans fats increase overall cholesterol levels.
- Increase Soluble Fiber:Foods like oatmeal, beans, and fruits can help reduce the absorption of cholesterol into your bloodstream.
- Regular Exercise:
- 30 minutes of daily exercise raises HDL and lowers LDL cholesterol.
- Maintain a Healthy Weight:
- Losing excess weight can help lower your total cholesterol, particularly LDL cholesterol.
- Avoid Smoking:
- Smoking decreases HDL cholesterol and raises heart disease risk while quitting can improve HDL levels.
- Limit Alcohol Consumption:
- Drinking alcohol in moderation can be beneficial for HDL cholesterol, but too much alcohol can lead to serious health problems, including high cholesterol.
- Medications:
- In some cases, lifestyle changes aren’t enough to lower cholesterol levels significantly. Your doctor may prescribe medications such as statins, bile-acid-binding resins, or other drugs to help manage cholesterol levels.
Regular Monitoring
Adults should have their cholesterol checked every four to six years, while those with high cholesterol or other risk factors may need more frequent testing.
Conclusion
Cholesterol plays a crucial role in your body, but maintaining the right balance is essential for heart health. By adopting a healthy lifestyle, including a balanced diet, regular exercise, and avoiding harmful habits like smoking, you can manage your cholesterol levels effectively. Regular monitoring and working closely with your healthcare provider will help you keep your cholesterol in check and reduce the risk of heart disease. Embrace these changes for a healthier, happier life.