Understanding the risk factors for heart disease is crucial, as it is one of the leading causes of death globally. By being aware of these risk factors, you can take proactive steps to protect your heart and overall well-being. While some risk factors are beyond your control, many are related to lifestyle choices and can be managed or modified. Here are 15 factors that increase your heart disease risk and tips on how to mitigate them.
1. High Blood Pressure
Hypertension, or high blood pressure, forces your heart to work harder than normal, increasing the risk of heart disease. Regular monitoring and lifestyle changes like reducing salt intake, exercising, and medication can help manage blood pressure levels.
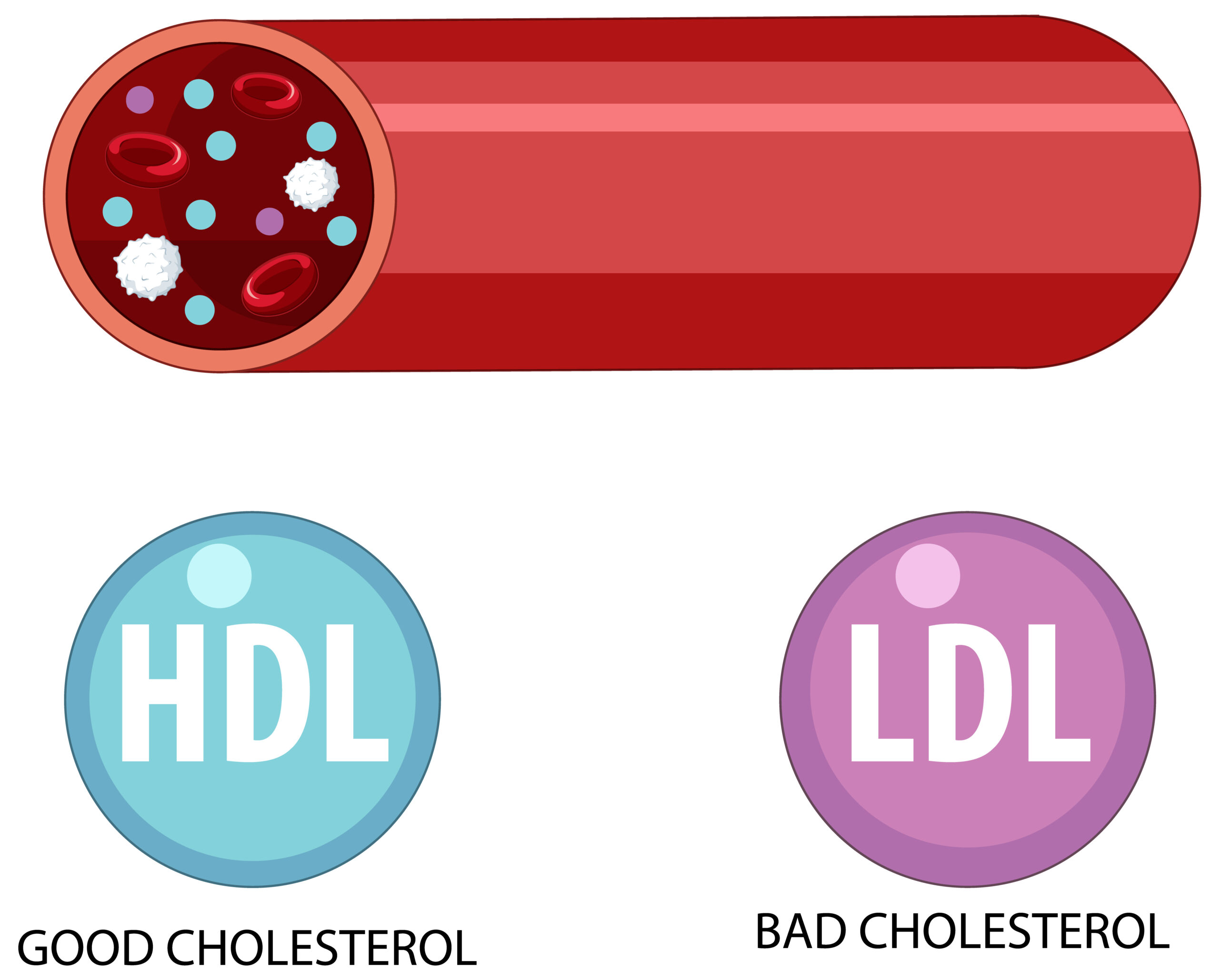
2. High Cholesterol
High LDL (bad) cholesterol levels can lead to a buildup of plaques in your arteries, increasing heart disease risk. A diet low in saturated fats, regular exercise, and medications can help maintain healthy cholesterol levels.
3. Diabetes
Diabetes significantly increases the risk of heart disease. Managing blood sugar levels through diet, exercise, and medication is crucial for reducing this risk.
4. Smoking
Smoking damages the lining of your arteries, leading to atherosclerosis and increasing the risk of heart disease. Improving heart health is one of the biggest benefits of quitting smoking.
5. Obesity
Excess body weight strains your heart and can lead to conditions like hypertension and diabetes. Maintaining a healthy weight through diet and exercise is essential for reducing heart disease risk.

6. Physical Inactivity
Sitting too much can lead to weight gain, increased blood pressure, and high cholesterol. Stay active to keep your body healthy. Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity weekly exercise to keep your heart healthy.
7. Unhealthy Diet
A diet high in saturated fats, trans fats, and cholesterol can raise your risk of heart disease. Focus on a diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats to protect your heart.
8. Excessive Alcohol Consumption
Drinking too much alcohol can raise blood pressure and contribute to heart disease. It is recommended to limit alcohol intake to moderate levels, which means up to one drink per day for women and up to two drinks per day for men.
9. Stress
Chronic stress may lead to behaviours and factors that increase heart disease risk, such as poor diet, physical inactivity, and smoking. Managing stress through relaxation techniques, exercise, and adequate sleep is important for heart health.
10. Family History
Having a family history of heart disease can raise your risk. While you can’t change your genetics, knowing your family history can motivate you to adopt a heart-healthy lifestyle and get regular check-ups.
11. Age
As you get older, your chances of developing heart disease go up. Regular health screenings and a heart-healthy lifestyle become even more important as you get older.
12. Gender
Men have a higher risk of developing heart disease at a younger age compared to women. However, the risk for women increases and becomes similar to men’s risk after menopause. Both men and women should focus on heart health throughout their lives.
13. Sleep Apnea
Sleep apnea, a condition where breathing repeatedly stops and starts during sleep, can increase blood pressure and heart disease risk. Treating sleep apnea through lifestyle changes or medical devices can help protect your heart.
14. Chronic Kidney Disease
Kidney disease can increase the risk of heart disease due to its effect on blood pressure and blood vessel health. Managing kidney disease through medication and lifestyle changes is important for reducing heart disease risk.
15. Poor Oral Health
Gum disease and other oral health issues have been linked to an increased risk of heart disease. Maintaining good oral hygiene through regular brushing, flossing, and dental check-ups can improve overall heart health.
Conclusion
Heart disease risk is influenced by a combination of genetic, lifestyle, and environmental factors. While you can’t change your age, gender, or family history, you can make lifestyle changes to reduce your risk significantly. Regular exercise, a healthy diet, quitting smoking, managing stress, and regular health check-ups are all essential steps for maintaining a healthy heart. By understanding and addressing these risk factors, you can take control of your heart health and work towards a longer, healthier life.