Heart disease remains a leading cause of death worldwide, affecting millions of individuals each year. Understanding this condition can help prevent, detect, and manage effectively. Here are 20 frequently asked questions about heart disease, answered to provide you with comprehensive information.
1. What is Heart Disease?
Heart disease refers to various types of heart conditions, including coronary artery disease, arrhythmias, heart valve disease, and heart failure. It primarily involves the narrowing or blockage of blood vessels that can lead to heart attacks, chest pain (angina), or stroke.
2. What Causes Heart Disease?
The most common cause of heart disease is the buildup of fatty deposits (plaque) in the arteries, known as atherosclerosis. Other factors include high blood pressure, high cholesterol, diabetes, obesity, smoking, a sedentary lifestyle, and genetic predisposition.
3. What Are the Symptoms of Heart Disease?
Symptoms vary depending on the type of heart disease but often include chest pain or discomfort, shortness of breath, pain in the neck, jaw, or back, lightheadedness, nausea, and fatigue. Women may experience more subtle symptoms like indigestion or back pain.
4. How is Heart Disease Diagnosed?
Diagnosis typically involves a physical exam, medical history review, and tests such as electrocardiograms (ECG), echocardiograms, stress tests, blood tests, and coronary angiography.
5. Can Heart Disease Be Prevented?
Yes, many forms of heart disease can be prevented through lifestyle changes such as maintaining a healthy diet, regular physical activity, quitting smoking, limiting alcohol intake, and managing stress. Regular health screenings are crucial to monitor blood pressure, cholesterol, and blood sugar levels.
6. What Are the Risk Factors for Heart Disease?
Key risk factors include high blood pressure, high cholesterol, diabetes, smoking, obesity, physical inactivity, unhealthy diet, excessive alcohol consumption, and a family history of heart disease.
7. Is Heart Disease Hereditary?
Genetics can play a significant role in heart disease. A family history of heart disease increases your risk, particularly if close relatives were diagnosed at a young age.

8. How Does Smoking Affect Heart Health?
Smoking damages the lining of the arteries, leading to atherosclerosis. It reduces the oxygen in your blood, raises blood pressure, and increases the tendency for blood to clot, all of which heighten the risk of heart disease and stroke.
9. Can Diet Impact Heart Disease?
Absolutely. A diet high in saturated fats, trans fats, cholesterol, and sodium can contribute to heart disease. Conversely, a diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats can help protect your heart.
10. What Role Does Exercise Play in Heart Health?
Regular physical activity strengthens the heart muscle, improves blood circulation, helps maintain a healthy weight, and reduces risk factors like high blood pressure and high cholesterol.
11. What is Hypertension and Its Link to Heart Disease?
Hypertension, or high blood pressure, forces the heart to work harder to pump blood. Over time, this extra effort can damage the heart and arteries, increasing the risk of heart attack, stroke, and heart failure.
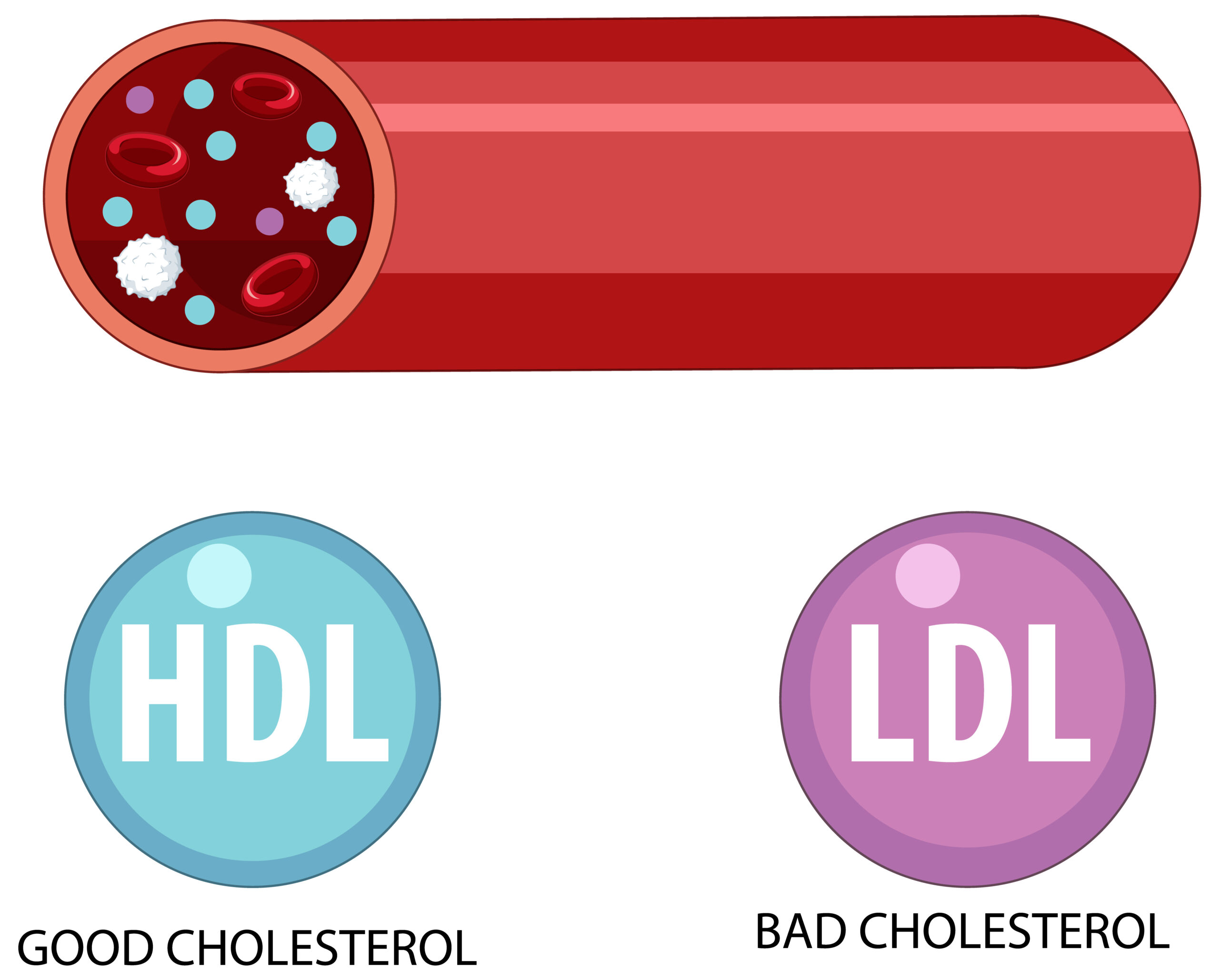
12. How Important is Cholesterol Management?
Managing cholesterol is crucial as high levels of low-density lipoprotein (LDL) cholesterol can lead to plaque buildup in arteries, while high levels of high-density lipoprotein (HDL) cholesterol can help remove it.
13. What is the Role of Stress in Heart Disease?
Chronic stress can lead to behaviors and factors that increase heart disease risk, such as overeating, physical inactivity, smoking, and high blood pressure. Stress management techniques can be beneficial for heart health.
14. How Does Diabetes Affect Heart Health?
Diabetes increases the risk of heart disease by contributing to high blood pressure, atherosclerosis, and damage to blood vessels. Proper management of blood sugar levels is essential for heart health.
15. What is Coronary Artery Disease (CAD)?
CAD is the most common type of heart disease. It occurs when the coronary arteries, which supply blood to the heart muscle, become narrowed or blocked due to plaque buildup, leading to reduced blood flow.
16. What is Heart Failure?
Heart failure occurs when the heart cannot pump enough blood to meet the body’s needs. It can result from various heart conditions that damage or weaken the heart, including coronary artery disease and hypertension.
17. Are There Different Types of Heart Disease?
Yes, heart disease encompasses various conditions, including coronary artery disease, arrhythmias, heart valve disease, cardiomyopathy, congenital heart defects, and pericardial disease.
18. Can Heart Disease Be Reversed?
While some damage from heart disease cannot be reversed, lifestyle changes, medications, and surgical interventions can manage symptoms, prevent further damage, and improve quality of life.
19. What are the Treatment Options for Heart Disease?
Treatment options depend on the specific condition and can include lifestyle changes, medications, medical procedures (such as angioplasty or bypass surgery), and, in severe cases, heart transplants.
20. Why is Regular Screening Important?
Regular screening helps detect risk factors and early signs of heart disease, allowing timely intervention to prevent complications and improve outcomes.
Understanding heart disease is crucial for taking proactive steps to maintain heart health. By staying informed, making healthy lifestyle choices, and seeking regular medical care, you can significantly reduce your risk and lead a healthier life.
This blog addresses these frequently asked questions to raise awareness about heart disease and promote a heart-healthy lifestyle. Stay tuned for more health tips and updates!