Skin conditions are common, and many people experience issues affecting their confidence and comfort. While some skin problems are contagious, others are not. Understanding non-contagious skin conditions can help you manage them effectively and improve your overall skin health.
1. Eczema (Atopic Dermatitis)
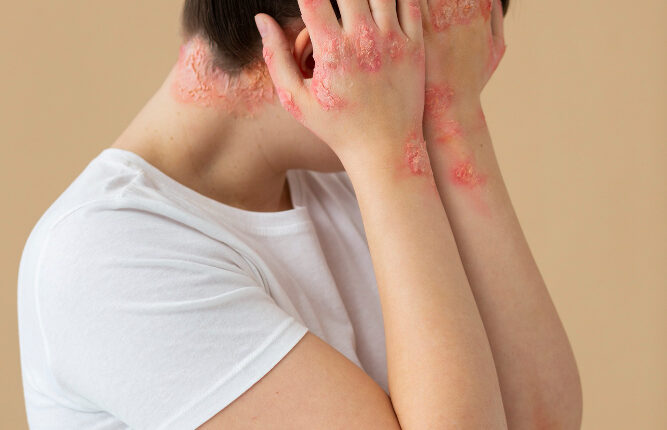
Eczema is a persistent skin condition that causes red, itchy, and inflamed patches of skin. It commonly appears on the face, hands, feet, and behind the knees. While the exact cause of eczema is unknown, it is believed to be related to a combination of genetic and environmental factors. Managing eczema involves moisturizing regularly, avoiding triggers such as harsh soaps and stress, and using prescribed medications like topical corticosteroids.
2. Psoriasis
Psoriasis is an autoimmune condition that causes the rapid buildup of skin cells, resulting in thick, scaly patches. These patches, known as plaques, are often red and covered with silvery scales. Psoriasis can appear anywhere on the body but is most common on the elbows, knees, scalp, and lower back. Treatment options include topical treatments, phototherapy, and systemic medications to reduce inflammation and slow cell turnover.
3. Rosacea
Rosacea is a chronic skin condition that primarily affects the face, causing redness, visible blood vessels, and sometimes small, red, pus-filled bumps. The exact cause of rosacea is unknown, but it can be triggered by factors such as hot drinks, spicy foods, alcohol, sun exposure, and stress. The treatment emphasizes symptom management using topical and oral medications, laser therapy, and making lifestyle adjustments to avoid triggers.
4. Vitiligo
Vitiligo is a condition where the skin loses its pigment cells, leading to white patches on various body parts. The cause of vitiligo is not entirely understood, but it is thought to be an autoimmune disorder. While there is no cure for vitiligo, treatments such as topical corticosteroids, light therapy, and skin grafting can help improve the appearance of the skin.

5. Hives (Urticaria)
Hives are red, itchy welts that can appear anywhere on the skin. They are often a reaction to an allergen or irritant, but sometimes the cause is unknown. Hives can be acute, lasting for less than six weeks, or chronic, lasting more than six weeks. Treatment includes antihistamines to reduce itching and swelling and avoiding known triggers.
6. Seborrheic Dermatitis
Seborrheic dermatitis is a common skin condition that causes red, scaly, and greasy patches, often on the scalp, face, and chest. When it affects the scalp, it is sometimes referred to as dandruff. The exact cause is unknown, but it is believed to be related to a combination of genetic, hormonal, and environmental factors. Treatment involves medicated shampoos, antifungal creams, and corticosteroids.
7. Lichen Planus
Lichen planus is an inflammatory condition that affects the skin and mucous membranes, causing purplish, flat-topped bumps. It can be itchy and often appears on the wrists, ankles, and lower back. The cause of lichen planus is unknown, but it is thought to involve an overactive immune response. Treatments include topical corticosteroids, oral medications, and light therapy to reduce inflammation and alleviate symptoms.
8. Alopecia Areata
Alopecia areata is an autoimmune disorder that causes hair loss, typically in round patches on the scalp. It is suggested that, in certain instances, this condition may have an impact on various parts of the body. Although the precise cause is not fully understood, it is thought to be connected to a mix of genetic and environmental influences. Treatment options include corticosteroids, topical immunotherapy, and other medications to stimulate hair growth and reduce inflammation.
9. Keratosis Pilaris
Keratosis pilaris is a common skin condition that causes small, rough bumps on the skin, typically on the upper arms, thighs, and buttocks. The accumulation of keratin, a protective skin protein, is what leads to this condition. While keratosis pilaris is harmless, it can be managed with moisturizing lotions, exfoliating treatments, and gentle skincare routines.
10. Melasma
Melasma is a condition that causes dark, discolored patches on the skin, often on the face. It is more common in women and is believed to be related to hormonal changes, such as those occurring during pregnancy or with the use of birth control pills. Sun exposure can also trigger or worsen melasma. Treatment includes sun protection, topical treatments like hydroquinone, and procedures such as chemical peels and laser therapy.
Conclusion
Understanding non-contagious skin conditions is crucial for managing them effectively and maintaining healthy skin. If you’re dealing with persistent or severe symptoms, reaching out to a dermatologist can provide you with the right diagnosis and treatment plan. By taking proactive steps and following professional advice, you can improve your skin health and overall well-being.