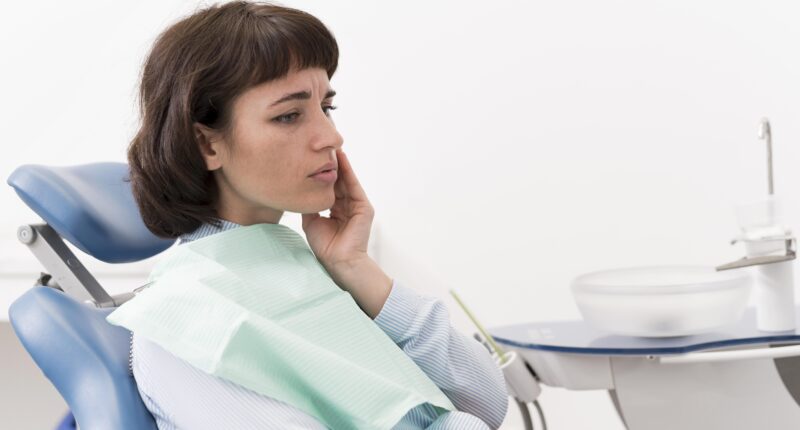
Infected root canals, also known as endodontic infections, can cause significant discomfort and pose risks to oral health if left untreated. We will discuss some of the causes, symptoms, treatment options, and preventive measures related to infected root canals, providing valuable insights into managing this dental condition effectively.
What is an Infected Root Canal?
An infected root canal occurs when bacteria enter the inner chamber (pulp) of a tooth, leading to inflammation, infection, and potential damage to the tooth structure. This can result from untreated tooth decay, dental trauma, cracks or fractures in the tooth, or previous dental procedures that compromise the tooth’s integrity.
Causes of Infected Root Canals
1. Untreated Tooth Decay: When dental caries (cavities) are left untreated, bacteria can penetrate the tooth’s enamel and dentin, reaching the pulp and causing infection.
2. Dental Trauma: Injuries such as cracks, fractures, or chips in the tooth can expose the pulp to bacteria, increasing the risk of infection.
3. Previous Dental Work: In some cases, previous dental procedures like fillings, crowns, or root canals themselves may fail over time, allowing bacteria to enter and infect the root canal system.
4. Poor Oral Hygiene: Inadequate oral hygiene practices, such as infrequent brushing, flossing, and dental check-ups, can contribute to the development of infected root canals by allowing plaque and bacteria to accumulate.
Symptoms of Infected Root Canals
1. Severe Tooth Pain: Persistent or throbbing pain, especially when biting or chewing, is a common symptom of an infected root canal.
2. Sensitivity to Temperature: Sensitivity to hot or cold foods and beverages, as well as sensitivity to air or pressure, may indicate a root canal infection.
3. Swelling and Tenderness: Swelling, redness, and tenderness in the gums around the affected tooth may occur due to inflammation and infection.
4. Pus or Abscess Formation: The presence of pus, a foul taste, or the development of a gum abscess (a pocket of infection) near the tooth may signal an infected root canal.
5. Discolouration of Tooth: Discolouration or darkening of the tooth, particularly if it is sudden or accompanied by other symptoms, can be a sign of pulp infection.
Treatment of Infected Root Canals
1. Root Canal Therapy: The primary treatment for infected root canals is root canal therapy (endodontic treatment). During this procedure, the infected pulp is removed, and the root canal system is cleaned, disinfected, and sealed with a dental filling or crown to prevent reinfection.
2. Antibiotics: In some cases of severe infection or systemic symptoms (e.g., fever), antibiotics may be prescribed to help control the infection and reduce inflammation.
3. Dental Restoration: Following root canal therapy, the tooth may require a permanent restoration such as a dental crown to restore its strength, function, and appearance.
Prevention of Infected Root Canals
1. Maintain Good Oral Hygiene: Brush your teeth at least twice a day, floss daily, and visit your dentist regularly for check-ups and cleanings to prevent tooth decay and gum disease.
2. Address Dental Issues Promptly: Seek prompt treatment for dental problems such as cavities, cracks, or trauma to prevent the spread of infection to the root canal.
3. Protective Mouthguards: Wear mouthguards during sports or activities that may pose a risk of dental injury to prevent fractures or trauma to teeth.
4. Avoid Tobacco and Excessive Sugar: Tobacco use and a high-sugar diet can increase the risk of dental problems, including infected root canals. Avoid tobacco products and limit sugary foods and drinks.
5. Regular Dental Check-ups: Schedule regular dental check-ups and X-rays to detect dental issues early and address them before they progress to infected root canals.
Infected root canals can cause significant pain and complications if not promptly treated. Recognising the causes, symptoms, and treatment options for infected root canals is crucial for maintaining oral health. By prioritising good oral hygiene, addressing dental issues promptly, and seeking professional dental care, individuals can prevent infected root canals and preserve their teeth for long-term health and function. Regular dental check-ups and consultations with a dentist are essential for early detection, diagnosis, and treatment of dental problems, including infected root canals.